We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
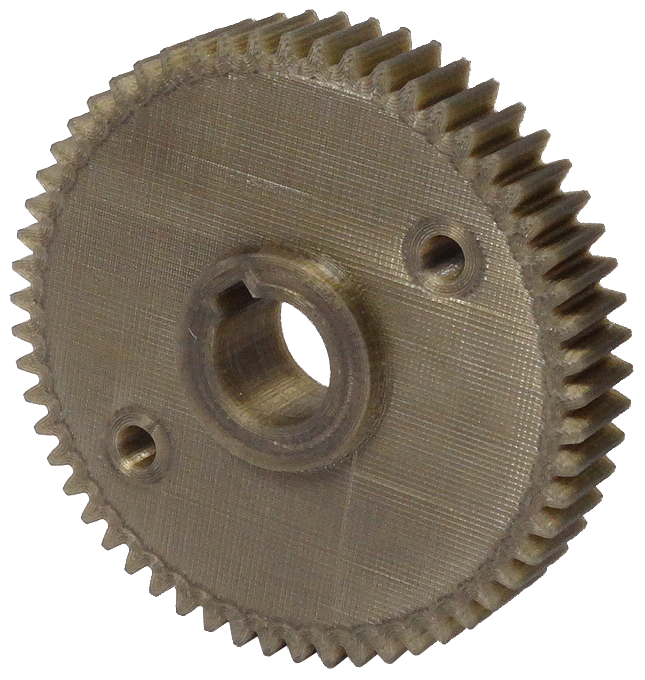
Rack/Pinion Set: Straight or Helical Teeth?

A rack is essentially a toothed bar that pairs with a gear wheel. Together, they convert rotational into linear movement, or vice versa. These features make the rack/pinion assembly essential in transmission systems.
There are two types of rack/pinion sets:
- Straight-tooth rack/pinion sets;
- Helical-tooth rack/pinion sets.
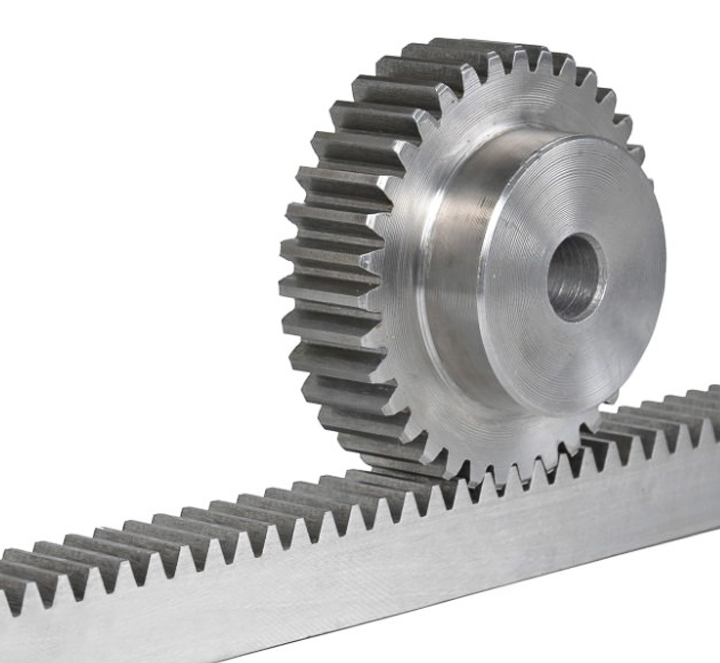

Straight-tooth Rack/Pinion Sets
In straight-tooth racks, the teeth are perpendicular to the rack's centreline while in gear wheels, the straight teeth are parallel to the wheel axis. This alignment ensures a direct and robust fit between the components.
This type of rack/pinion sets is the most common due to its simple geometry, enabling more accessible and cost-effective manufacturing, installation and maintenance processes.
Helical-tooth Rack/Pinion Sets
Helical rack/pinion sets, despite having the same role as the previous ones, have additional advantages.
Due to their 20º pressure angle, increases the number of teeth in contact between the rack and gear wheel. They therefore offer greater mechanical strength and load transmission capacity.
The precision helical rack/pinion set reduces noise levels compared to straight-tooth rack/pinion set, especially at higher speeds.
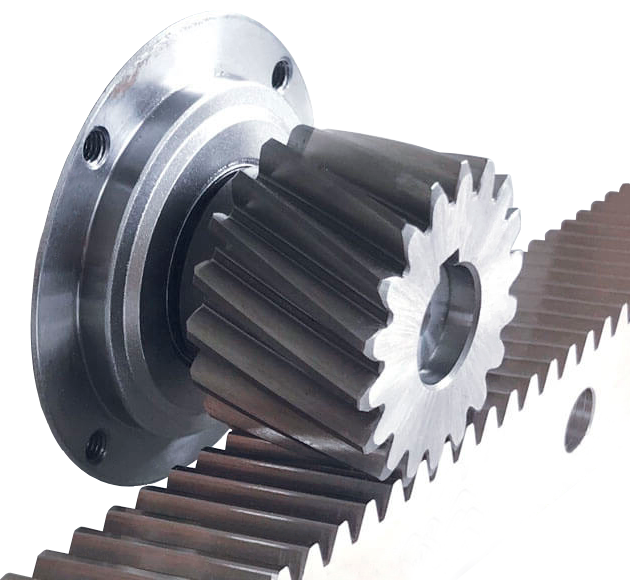

Regardless of the type, the rack teeth must match the size and shape of the gear teeth.
Mechanical resistance is the strong point of the rack/pinion sets, delivering robustness, high torque transmission and linear speed.
The main difference between helical and straight tooth rack/pinion sets lies in the shape and engagement of the teeth. Choosing between them depends on the specific requirements of each application, considering factors such as precision, smoothness, noise levels and durability.
Reiman offers both types of rack/pinion sets in various sizes and materials, at affordable prices, to better respond and facilitate industrial processes involving motion mechanisms.
3D Printing - FDM Technology
EON PEKK

3D Printing - SLA Technology
Hyperion Resistent