We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
What is FDM? (Fused Deposition Modeling)
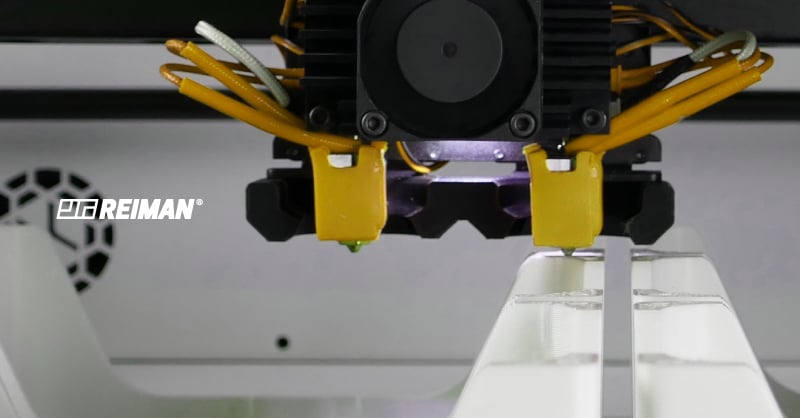

The term FDM was born in the late 1980s and is currently the most widely used 3D printing technology in the world. When it was created, this technology was used for the construction of machines, but after some transformations throughout its evolution, FDM is today a process of manufacturing and production of parts of stable dimension.
The production of the parts is made through an extrusion process where the object is built by depositing the softened material layer by layer. The materials used are thermoplastic filaments. These materials are introduced in a 3D printer that is programmed with the temperature that must be reached. As soon as it reaches the ideal temperature, the process begins and the material begins to soften. As previously mentioned, this material, after softening, is deposited layer by layer in determined places where it cools and solidifies. This is a repetitive process, which requires several passages until the parts are complete.
Recently, Reiman launched its additive manufacturing service - RMN Additive - and there is a strong bet on the FDM process. As such, it provides a set of materials compatible with the process, from the most used to the less common, constituting a wider offer.
The materials used in this process can vary between:
- Thermoplastics of goods
- Thermoplastics for engineering
- High-performance thermoplastics
Types of materials that RMN Additive works with:
PETG –Polyethylene Terephthalate Modified with Glycol
This is a material with significant durability, which makes it great for printing mechanical components. In addition to its excellent processing characteristics, it also has high strength and malleability, good heat resistance, low thermal expansion, and great water resistance. It is mostly applied in:
- Mechanical components
- Waterproof components
- Holders and cases
PC - Polycarbonate
This is a very durable material, with high impact tenacity and heat resistance. As it is a plastic of engineering, it is mostly used for more robust applications such as:
- High strength parts
- Heat resistant prints
- Housings for electronic components
ABS / ASA- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene / Acrylonitrile and Styrene Acrylate
These are materials with very similar mechanical properties, however, ASA is more UV resistant. In addition, ASA is also very resistant to heat, moisture, and impact. This material is mostly used for:
- Outdoor components
- Covers and protective cases
- Replacement parts
- Prototypes
PLA- Polylactide
Polylactic Acid is an ideal biodegradable thermoplastic for the manufacture of large and detailed objects due to its low thermal expansion. It should not be used on parts that need thermal resistance, since it begins to lose mechanical resistance at about 60ºC. This material is mostly used for:
- Decorative and cosplay props
- Prototypes
- Toys and figures of action
- Dimensional accurate assemblies
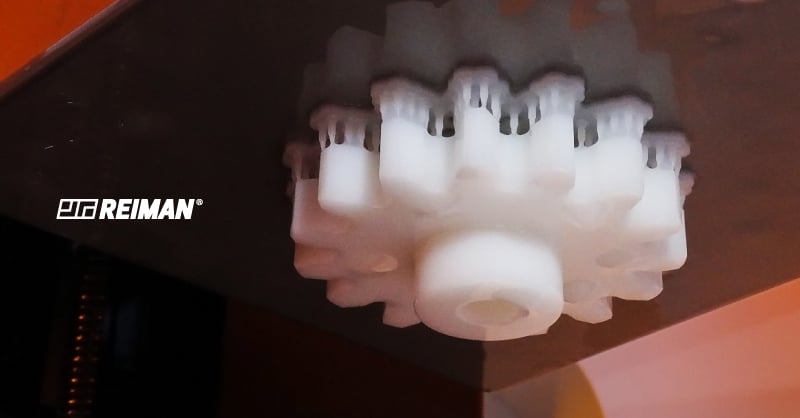
Nylon
Nylon is a very strong and rigid plastic with excellent thermal and chemical resistance. With good self-lubricating properties, this material has great electrical insulation and is corrosion-resistant, making it very useful for the following applications:
- Gears, screws, and nuts
- Cable ties
- Electric Housings
Nylon with chopped carbon fiber
This material results from the fusion of Nylon with carbon microfibers. It is a very versatile material that offers mechanical resistance, tenacity and chemical resistance while producing accurate parts with an impeccable surface finish and still with dimensional stability. Thus, it is mostly applied in:
- Plastic parts replacement
- Sensor mounts
- Housings
- Cosmetic Prototypes
Advantages
- Speed -Due to the number of technologies available for this process, FDM has a very fast production and consequently short delivery times.
- Versatility - The nature of the materials in this service can be very different among them and therefore, through FDM it is possible to obtain prototypes, models, and objects completely different from each other.
- Accuracy - This process has the ability to produce very complex geometries and still reach internal holes that would be unreachable with other technologies.
- Low costs - The fast production capacity, combined with the best technologies, lower prices, and more efficient consumption, make this service very accessible at the price level.
-
- Efficiency - It is an environmentally friendly and efficient process since it hardly causes any noise and has a very efficient consumption.