We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
What is SLA? (Stereolithography)

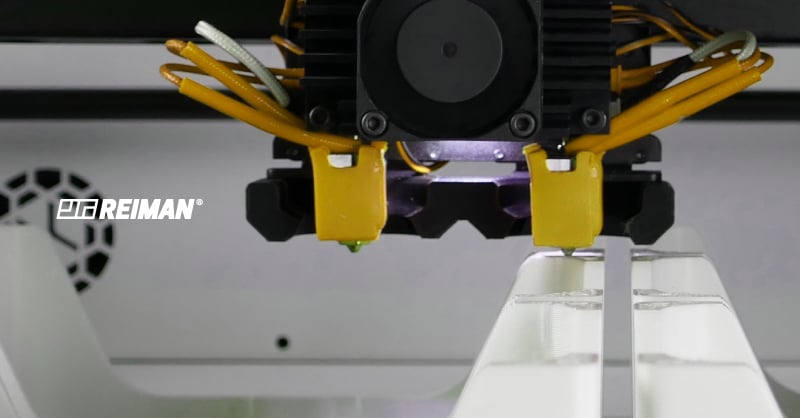
In 1986 the term SLA was born, the first 3D printing technology. Since then, it has undergone some evolutions and through it is possible to create and obtain models and objects of the most varied forms, with great precision. Its operation consists in creating these same objects through a laser that gradually solidifies the photopolymer.
Reiman, recently launched its additive manufacturing service – RMN Additive - and has a strong focus on SLA technology. As previously mentioned, this process works through resin polymerization and it can obtain different shapes and thicknesses according to its type.
The resins used in this process can vary between:
Standard Resins
The standard resin is a material with high resolution, resistance, precision and great surface finish, which makes it perfect for more demanding applications, creating accurate and robust parts. Therefore, the standard resin is ideal for:
- Highly detailed models
- Flow Study
- Translucent parts
- Optics and lighting
- Prototypes
Flexible Resin
The flexible resin balances the softness with the resistance, which makes it capable of resisting bending and compression. This is the perfect material for:
- Consumer goods prototyping
- Compliant features for robotics
- Medical devices and anatomical models
- Seals, gaskets and masks
Elastic Resin
The elastic resin is a soft material that simulates silicone, capable of producing parts that bend, stretch, compress and that hold up to repeated cycles without tearing and return to its original shape. See some examples:
- Consumer goods prototyping
- Compliant features for robotics
- Medical devices and anatomical models
- Stretchable enclosures and casing
Durable Resin
This material adapts to squeezable parts and low-friction assemblies. It is easily malleable, lubricious and impact resistant. The main applications go through:
- Housings and casings
- Impact-resistant fastening jigs and fixtures
- Squeezable prototypes
- Low friction assemblies
Rigid Resin
The rigid resin is filled with glass particles and therefore has great rigidity and resistance. The finishing of the pieces made from this resin is smooth and polished. It is mostly used in:
- Turbines and fan blades
- Jigs, fixtures and tooling
- Manifolds
- Electrical casings and automotive housings
Tough Resin
This is a material that is characterized by its robustness, functionality and dynamics. These characteristics make this resin able to withstand compression, stretching and bending without breaking. Here are some examples of its application:
- Housings and enclosures.
- Jigs and fixtures and accessories
- Connectors
- Wear-and-tear prototypes
High-temperature Resin
High-Temperature resin is a material that offers a heat deflection temperature of up to 238ºC, making it perfect to manufacture detailed, precise parts with high-temperature resistance. See some examples:
- Hot air, gas, and fluid flow
- Heat resistant mounts, housings, and fixtures
- Molds and inserts
Biocompatible Resin
The biocompatible resin is a material developed to offer resistance to solvents and autoclaves, as well as the exceptional quality of parts, precision and performance. This resin is CE certified and meets Class I requirements for Medical Devices. It is mostly used in:
- Surgical Guides
- Pilot drill guides
- Drilling templates
- Device sizing templates
Main advantages associated with the process:
- Speed - Resin polymerization is a relatively quick process and therefore it is possible to obtain several parts in a short period of time, depending always on the complexity that the piece requires, obviously. The SLA is, therefore, a process with profitable production.
-
- Personalization -Through the SLA it is possible to design and obtain an infinite number of parts and prototypes. As previously mentioned, there are many types of resin and therefore it is possible to make several creations.
-
- Automated process - This is an automated process since you just enter the data into the program and the printer automatically starts printing.
-
-
- Cost savings - It is not an expensive process since the materials that integrate it do not entail very high costs.
-