We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies. Learn more.
Sustainable 3D Printing: Giving New Life to Filaments at RMN Additive

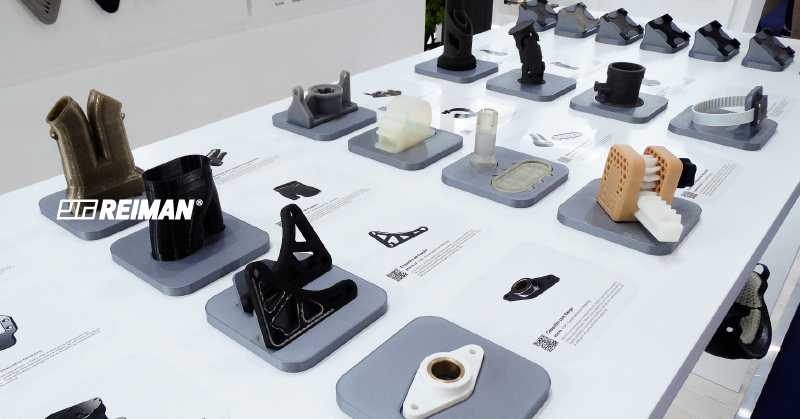
The world of 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has exploded in popularity, offering tremendous potential for innovation, rapid prototyping and serial production in the industrial sector.
But what happens to all the filament waste when a project is completed?
Traditionally, these filaments end up in landfills, contributing to the growing problem of plastic waste.
At RMN Additive, we approach this challenge differently. We separate the waste from our filaments, each with unique properties, to generate new printing materials. This sustainable practice not only reduces environmental impact but also offers economic advantages.
By providing plastic, we help reduce the dependence on virgin plastic, which requires the extraction of fossil fuels, while generating harmful emissions. In this way, the principles of the circular economy are kept in practice for as long as possible.
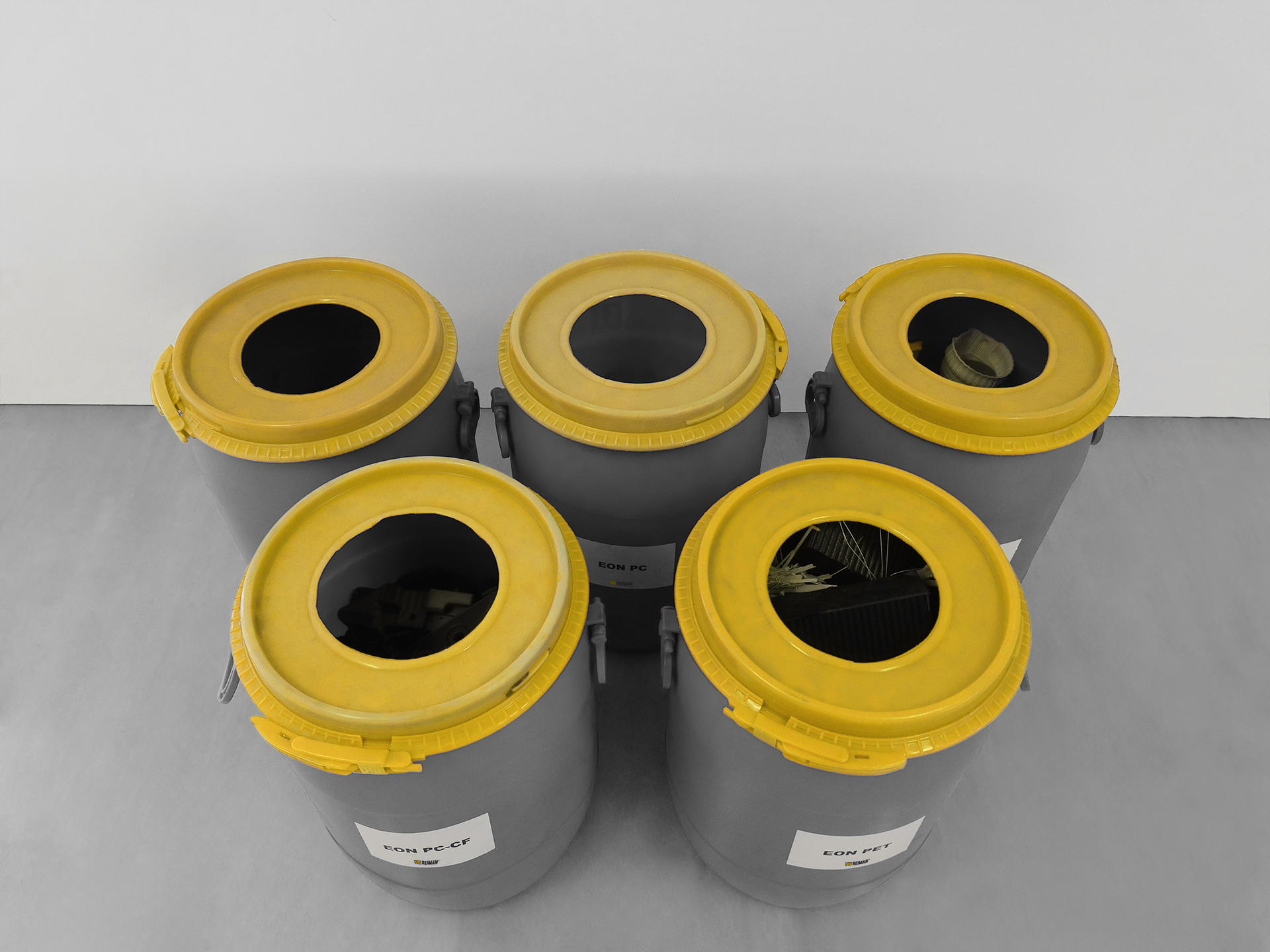






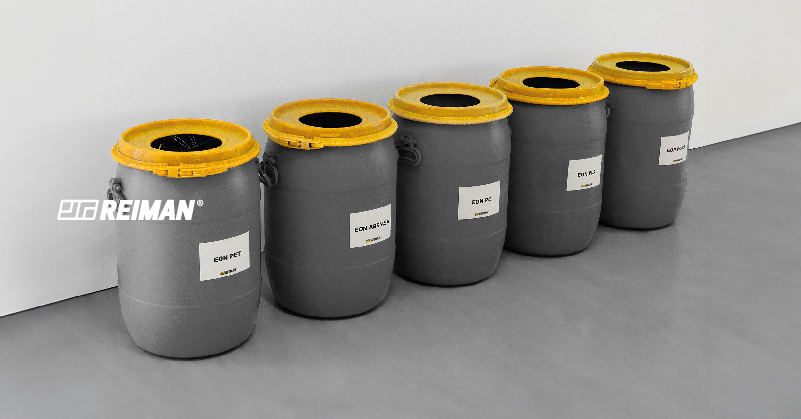
How does the process of reusing filaments work?
- Collection - The filaments are separated by material type. Thermoplastics are most commonly reused as their properties do not degrade.
- Grinding - The filaments of each material are then crushed, this reduction in size is crucial as it ensures that the material can be melted consistently and evenly.
- Extrusion - The crushed material is extruded and transformed into new filaments for new 3D printing cartridges.
All of these recycling processes involve control and quality measures. If applicable, some cleaning processes may be necessary to remove any debris, powders or other contaminants that could affect the quality of the recycled filament.
Important Considerations:
- Color and Texture Variations
Since recycled filaments can come from others with various colors and textures, compared to virgin filaments, they may present slight variations in color and texture. This aesthetic difference typically does not affect the performance and productivity of the filament and the equipment.
- 3D Printer Calibration
Due to potential variations in material properties, it may be necessary to calibrate the printer settings to achieve optimised results.